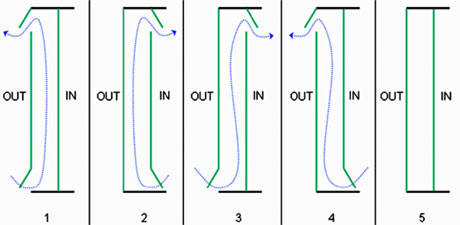
Ventilation mode of the cavity
The ventilation mode refers to the origin and the destination of the air circulating in the ventilated cavity. The ventilation mode is independent of the type of ventilation applied (the first classificatory criterion presented).
Not all of the facades are capable of adopting all of the ventilation modes described here. At a given moment, a facade is characterised by only a single ventilation mode. However, a facade can adopt several ventilation modes at different moments, depending on whether or not certain components integrated into the facade permit it (for example operable openings).
One must distinguish between the following 5 main ventilation modes
(see Fig. below):
1. Outdoor air curtain
In this ventilation mode, the air introduced into the cavity comes from the outside and is immediately rejected towards the outside. The ventilation of the cavity therefore forms an air curtain enveloping the outside facade.
2. Indoor air curtain
The air comes from the inside of the room and is returned to the inside of the room or via the ventilation system. The ventilation of the cavity therefore forms an air curtain enveloping the indoor facade.
3. Air supply
The ventilation of the facade is created with outdoor air. This air is then brought to the inside of the room or into the ventilation system. The ventilation of the facade thus makes it possible to supply the building with air.
4. Air exhaust
The air comes from the inside of the room and is evacuated towards the outside. The ventilation of the facade thus makes it possible to evacuate the air from the building.
5. Buffer zone
This ventilation mode is distinctive inasmuch as each of the skins of the double facade is made airtight. The cavity thus forms a buffer zone between the inside and the outside, with no ventilation of the cavity being possible.